In modern healthcare, where technology and patient care intersect, the seamless integration of Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) (healthcare integration) with enterprise systems is revolutionizing how we approach health management. In the United States—a landscape marked by intricate healthcare networks and diverse patient needs—achieving true interoperability has become necessary. But how does this integration work, and why does it matter?
In this blog, we’ll discuss EMR interoperability and how its potential can redefine patient care for the better.
Table of Contents
Why Do Healthcare Providers Need EMR and Enterprise System Integration?
The U.S. healthcare system, renowned for its advanced capabilities, faces a critical challenge today: the lack of seamless integration between Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) and enterprise systems. Critical to clinical and administrative functions, these systems operate in isolation and compromise efficiency, patient care, and even outcomes.
Imagine a patient navigating this system—a network of doctors, specialists, insurers, and administrative staff. At every step, a flood of data is generated, from clinical notes to diagnostic tests, insurance claims, and appointment schedules. Yet, instead of forming a cohesive narrative, this data remains scattered across various platforms. The result? Inefficiencies, errors, and an uphill battle for both patients and providers.
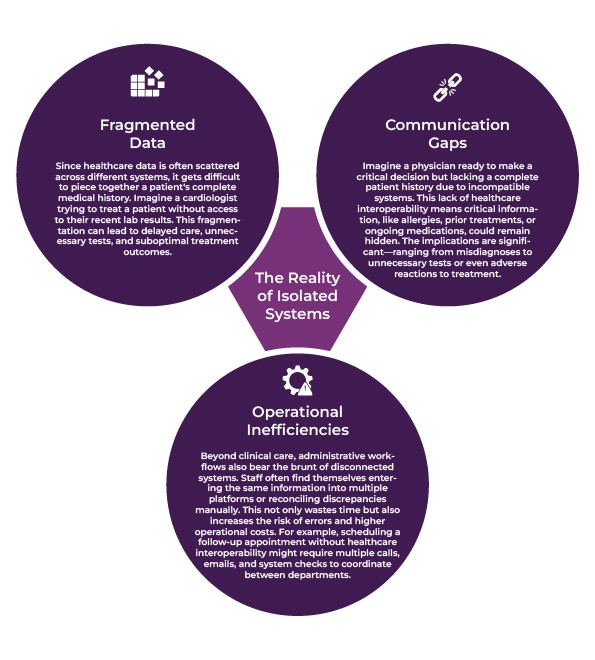
The Reality of Isolated Systems
1. Fragmented Data
Since healthcare data is often scattered across different systems, it gets difficult to piece together a patient’s complete medical history. Imagine a cardiologist trying to treat a patient without access to their recent lab results. This fragmentation can lead to delayed care, unnecessary tests, and suboptimal treatment outcomes.
2. Communication Gaps
Imagine a physician ready to make a critical decision but lacking a complete patient history due to incompatible systems. This lack of interoperability means critical information, like allergies, prior treatments, or ongoing medications, could remain hidden. The implications are significant—ranging from misdiagnoses to unnecessary tests or even adverse reactions to treatment.
3. Operational Inefficiencies
Beyond clinical care, administrative workflows also bear the brunt of disconnected systems. Staff often find themselves entering the same information into multiple platforms or reconciling discrepancies manually. This not only wastes time but also increases the risk of errors and higher operational costs. For example, scheduling a follow-up appointment without healthcare interoperability might require multiple calls, emails, and system checks to coordinate between departments.
Why Integration Matters ?
By connecting EMRs and enterprise systems, the healthcare industry can create a unified flow of information that benefits every stakeholder. Integrated systems enable healthcare interoperability and enhance patient outcomes. For patients, this means fewer delays, more accurate diagnoses, and a smoother care journey. For providers, it translates to reduced administrative burdens and better-informed decision-making.
How to Unlock the True Potential of Healthcare with EMR and Enterprise System Integration?
Integrating Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) with enterprise systems represents more than a technical enhancement—it’s a paradigm shift toward a patient-centric, efficient, and compliant healthcare model. Let’s explore how this healthcare interoperability can change the US healthcare sector:
1. Better Patient Care
Imagine a healthcare system where every critical piece of patient information—from allergies to past treatments—is at a doctor’s fingertips, no matter the time or place. This is the reality that EMR and enterprise integration can create, which leads to:
- Sharper Diagnoses: With a consolidated view of medical histories, lab results, and imaging studies, healthcare providers can make more precise and timely decisions.

- Tailored Treatment Plans: Access to rich datasets empowers doctors to craft customized treatment strategies. For example, an oncologist can instantly combine genetic data with previous treatment responses to propose a targeted cancer therapy.

- Life-Saving Speed in Emergencies: When every second counts, having immediate access to critical details can make the difference between life and death.

2. Efficient Operational Efficiency
Integration serves as a powerful tool for streamlining operations, which may include:
- Insurance Processes Simplified: Healthcare providers can reduce wait times by automating tasks like insurance verification.

- Streamlined Scheduling: By integrating systems, healthcare providers can create more efficient schedules, reduce wait times, and improve patient satisfaction.

- Paperless Precision: By replacing redundant paperwork with digital workflows, hospitals and clinics can focus their resources on patient care rather than administrative burden.

For example, in a bustling urban hospital with integrated systems, patients can book an appointment online, have their insurance verified automatically, and be greeted by a care team that already knows their history—all with minimal wait times.
3. Meeting Compliance with Confidence
Regulatory compliance in the US healthcare sector is no small feat. HIPAA mandates stringent data security to protect patient health information (PHI). However, healthcare interoperability can make these challenges more manageable:
- Secure Data Sharing: By leveraging encryption protocols like AES and TLS, healthcare organizations can securely transmit sensitive patient data and minimize the threat of cyberattacks.

- Access Control: Providers can safeguard sensitive systems from unauthorized access by enforcing role-based and context-aware policies.

- Regulatory Adherence: Healthcare solutions, like AERIS, align with the standards of HIPAA and GDPR. Therefore, it helps healthcare organizations meet legal requirements without disrupting operations.

For example, even a small rural clinic can meet federal reporting standards and achieve regulatory compliance on par with a cutting-edge urban hospital. Solutions like AERIS empower providers of all sizes to enhance care delivery while maintaining security and compliance with confidence.
4. Cost Reduction
One common myth surrounding healthcare interoperability is that it’s expensive. However, the reality is quite different when you consider the long-term benefits. By reducing redundancies and streamlining operational workflows, these coordinated efforts ultimately lead to significant cost savings.
The Role of Patient Engagement in Integration
In healthcare, patients are not just recipients of care; they are active participants. Therefore, patient engagement plays a pivotal role in the success of integrated healthcare systems. Below is a more detailed breakdown of how integration and healthcare interoperability promote patient engagement:
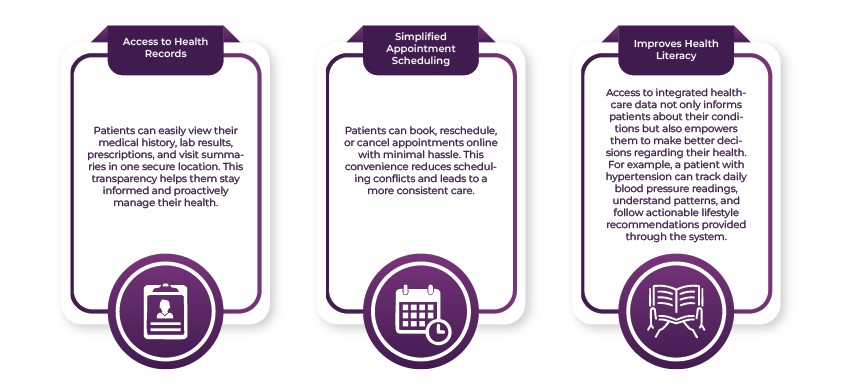
- Access to Health Records: Patients can easily view their medical history, lab results, prescriptions, and visit summaries in one secure location. This transparency helps them stay informed and proactively manage their health.
- Simplified Appointment Scheduling: Patients can book, reschedule, or cancel appointments online with minimal hassle. This convenience reduces scheduling conflicts and leads to a more consistent care.
- Improves Health Literacy: Access to integrated healthcare data not only informs patients about their conditions but also empowers them to make better decisions regarding their health. For example, a patient with hypertension can track daily blood pressure readings, understand patterns, and follow actionable lifestyle recommendations provided through the system.
Therefore, by demystifying medical information, integrated systems and healthcare interoperability help patients feel more confident and engaged in their treatment plans.
Why Patient Engagement Matters in Integration?
An engaged patient is more likely to comply with treatments, seek preventative care, and maintain open communication with their providers. By facilitating transparency, collaboration, and education, integrated systems enhance the patient experience while driving better health outcomes.
What Are the Best Practices for Seamless Integration?
Integrating electronic medical records (EMRs) with enterprise systems can help you achieve long-term operational and clinical improvements. Below is a detailed discussion of key strategies for successful implementation.
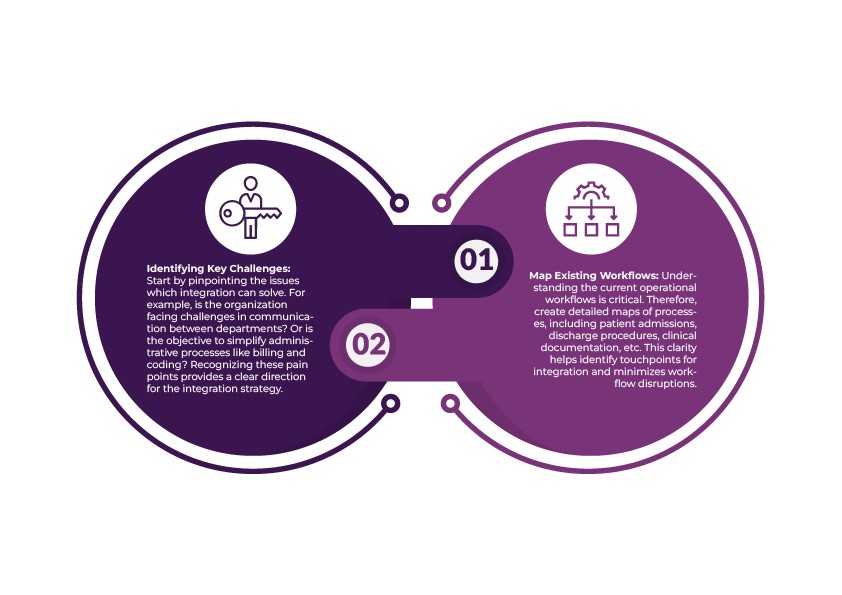
1. Conducting a Needs Assessment
Firstly, healthcare organizations must thoroughly evaluate their requirements. This step helps identify potential gaps that integration can address.
- Identifying Key Challenges: Start by pinpointing the issues which integration can solve. For example, is the organization facing challenges in communication between departments? Or is the objective to simplify administrative processes like billing and coding? Recognizing these pain points provides a clear direction for the integration strategy.
- Map Existing Workflows: Understanding the current operational workflows is critical. Therefore, create detailed maps of processes, including patient admissions, discharge procedures, clinical documentation, etc. This clarity helps identify touchpoints for integration and minimizes workflow disruptions.
2. Choosing the Right Provider
Selecting the right technology partner is one of the most critical decisions in the integration process. Their capabilities and expertise directly impact the success of the project.
- Interoperability Standards Compliance: It’s better to work with providers who align with industry standards like HL7 (Health Level Seven) and FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources). These standards facilitate seamless data exchange between systems.
- Scalability: Healthcare organizations grow over time, whether through expanding patient bases, adding new departments, or adopting additional technologies. Therefore, your provider should offer solutions that can adapt to such growth without requiring significant overhauls.
3. Phased Implementation
A phased approach to integration reduces risks, mitigates disruptions, and facilitates smoother transitions across departments.
- Pilot Programs: Launch the integration in a single department or with a small set of workflows as a trial. For example, starting with the emergency department can help test critical functionalities in a high-pressure environment.
- Incremental Rollouts: Once the pilot program demonstrates success, expand the integration gradually to other departments or systems. Addressing challenges as they arise during these incremental rollouts reduces the likelihood of widespread issues and helps maintain staff confidence.
4. Stakeholder Involvement
Active involvement from all stakeholders—administrators, clinicians, IT staff, and even patients—is necessary for successful integration. Therefore:
- Regular Meetings: Hold meetings to discuss progress, address concerns, and update stakeholders on milestones. Transparent communication keeps everyone aligned and reduces misunderstandings.
- Feedback Sessions: Create opportunities for stakeholders to provide feedback, whether through surveys, focus groups, or one-on-one interviews.
These best practices not only streamline workflows but also pave the way for improved patient care, operational efficiency, and organizational success.
What is AERIS and How it Facilitates Seamless Healthcare Integration
AERIS, developed by HelixBeat, is a robust solution built to support seamless and adaptable real-time data sharing across diverse platforms, systems, and organizations. It is designed to accommodate varying data formats, protocols, and requirements, thus supporting interoperability and flexibility. This capability is especially vital in industries like healthcare, where the need for real-time, accurate, and reliable data exchange is highly important for operational efficiency and decision-making.
Key Features:
1. Core Interoperability Framework
a. Standards-Compliant Communication
AERIS is built on the globally recognized interoperability standard HL7 FHIR, which facilitates consistent and structured data exchange across different Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems. By adhering to these standards, AERIS enables healthcare providers to integrate and access patient data across diverse platforms without friction. This approach simplifies sharing critical information like medical histories, prescriptions, and lab results.
b. Protocol Versatility
AERIS communicates using various data exchange protocols, including HTTP, FTP, MQTT, and SOAP. This flexibility enables the system to connect seamlessly with both older, legacy systems and newer, cloud-based platforms. By accommodating diverse technological infrastructures, AERIS bridges the gap between traditional and modern healthcare systems. As a result, it creates a unified ecosystem for data sharing.
c. Semantic Consistency
AERIS employs standardized terminologies and ontologies to maintain the integrity and usability of data. These standards keep the meaning of the data consistent, regardless of where or how it is used. Thus, by aligning data formats and definitions, AERIS eliminates ambiguities and supports accurate interpretation across multiple platforms.
2. Adaptability and Scalability
a. Dynamic Data Integration
AERIS combines new data formats and structures without disrupting existing workflows. Therefore, healthcare providers can seamlessly adopt cutting-edge diagnostic tools, advanced medical devices, or innovative software solutions without needing extensive reconfiguration of their systems.
b. Modular Flexibility
AERIS is designed with plug-and-play modularity. Thus, providers can easily add or remove components based on organizational needs. This modular architecture reduces operational downtime during system integrations or upgrades.
c. Future-Ready Scalability
Healthcare providers often encounter varying data and service demands, especially during unexpected events like pandemics or seasonal spikes in patient volume. AERIS can accommodate these fluctuations and help providers maintain consistent performance as the organization expands or faces increased operational pressures.
3. Data Management
a. Real-Time Data Exchange
AERIS facilitates instantaneous communication across healthcare systems. For example, when a patient completes a CT scan, the scan results are immediately transmitted to the referring physician’s system. This eliminates delays that could occur in manual sharing or siloed systems. In critical situations like diagnosing a stroke or managing trauma, this real-time exchange significantly improves patient outcomes, as providers can make quick interventions.
b. Data Normalization
In healthcare environments where multiple software systems coexist, data often arrives in various formats, which can complicate its analysis and usage. However, AERIS tackles this challenge by converting incoming data into a unified structure. This standardized format facilitates easier integration with electronic health records (EHRs), analytics platforms, and other applications.
c. Master Data Management (MDM)
Managing patient information is critical for avoiding errors and duplication. Therefore, AERIS implements Master Data Management to consolidate and maintain high-quality data across the organization. By establishing a unified source of truth, AERIS reduces inconsistencies, like multiple entries for the same patient under different spellings or identifiers. This unified dataset strengthens coordination among teams and builds confidence in the decision-making process.
4. Security and Compliance
a. Encryption
AERIS leverages advanced encryption methods like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) to protect sensitive data both in transit and at rest. These encryption protocols convert data into unreadable formats. Therefore, it’s challenging for unauthorized entities to decipher or misuse the information. Whether healthcare data is transferred between systems or stored within databases, AERIS employs these techniques to fortify data privacy and confidentiality.
b. Access Control
AERIS incorporates comprehensive access control mechanisms to prevent unauthorized interactions with the system. Using role-based access policies, the platform assigns permissions based on a user’s responsibilities and role within the organization. Also, context-aware access policies consider time, location, and device used to access the system. Collectively, these measures limit system access to appropriate personnel and improve overall security.
c. Audit Trails
AERIS meticulously records every user interaction and system event through detailed audit trails. These logs serve as a transparent record that tracks who accessed the system, what changes were made, and when these actions occurred. Such a comprehensive trail not only supports accountability but also simplifies investigations in case of discrepancies or potential breaches. It also strengthens organizational compliance efforts by providing clear evidence of operational integrity.
d. Regulatory Adherence
Healthcare organizations must navigate a complex web of legal and regulatory standards to manage patient data responsibly. AERIS aligns its framework with global standards like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) and GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation). This helps healthcare providers handle patient information as per established legal requirements. Thus, AERIS mitigates risks associated with non-compliance and promotes responsible data governance.
5. Integration Capabilities
a. API Gateway
AERIS functions as a centralized management hub for API interactions. This feature simplifies and secures the exchange of information between disparate systems. For example, if each system in a hospital has its own way of storing and sharing information, AERIS helps these systems communicate and share information smoothly, even if they speak different “languages.” Thus, EHRs, pharmacies, and diagnostic labs can interact smoothly without requiring major modifications to their underlying architectures.
b. Data Adapters
AERIS features custom-built data adapters designed to connect modern and legacy systems, as well as IoT devices and cloud-based applications. For example, a wearable heart monitor might generate health metrics in a proprietary format. AERIS processes and converts this data into a format the EHR system understands, thus providing real-time health insights.
c. Cross-Domain Interoperability
AERIS extends its integration capabilities beyond healthcare providers by facilitating collaboration between stakeholders like insurance companies, pharmacies, and public health agencies. For example, when a hospital submits a claim for a patient, AERIS automatically shares relevant medical data with the insurance company while safeguarding patient privacy. This streamlined approach minimizes delays, improves operational efficiency, and enhances decision-making across interconnected industries.
6. Automation and Intelligence
a. AI/ML Integration
AERIS leverages AI and ML to provide more accurate, efficient, and personalized services. Therefore, by analyzing vast amounts of healthcare data, AERIS can uncover patterns, predict health trends, and flag potential risks. For example, the system might analyze a patient’s medical history and current condition to forecast the likelihood of complications or suggest preventive measures.
b. Workflow Automation for Streamlined Operations
Repetitive administrative tasks, like updating electronic health records (EHRs), generating compliance reports, or coordinating care between departments, can consume valuable time and resources. AERIS simplifies these processes by automating them. For example, when a healthcare provider inputs new patient information, the system automatically synchronizes this data across relevant records and minimizes the risk of human error.
c. Dynamic Error Management
Errors in healthcare data—such as missing fields or incorrectly formatted entries—can lead to delays and miscommunications. AERIS actively monitors for such inconsistencies and corrects them in real-time. For example, if a required field in a patient’s record is left blank, the system alerts the user or fills it with appropriate data based on contextual analysis. Similarly, it standardizes data formats and enhances interoperability between systems.
7. Monitoring and Analytics
a. Real-Time Monitoring
Real-time dashboards act as a centralized hub that offers a comprehensive view of ongoing operations. For example, healthcare systems can use AERIS to track patient records between providers and identify bottlenecks in real-time. This continuous visibility helps stakeholders stay informed, make immediate adjustments, and maintain operational efficiency without delays.
b. Proactive Alerts
AERIS sends timely notifications to stakeholders regarding potential issues, such as system vulnerabilities or anticipated downtimes. These alerts help stakeholders take preemptive actions to address or mitigate risks. This proactive approach minimizes disruption and enhances the overall system reliability.
Practical Tips for a Smooth Transition to AERIS
Transitioning to a platform like AERIS is a big move, but it doesn’t have to be scary. Here are some practical tips to make the adoption process seamless:
1. Start Small and Scale Up
Start with a pilot project, like implementing AERIS in a single department or focusing on a specific data flow. Demonstrating early benefits in a controlled environment can simplify expansion across other areas.
2. Involve Stakeholders Early
Engage clinicians, administrative staff, IT teams, and compliance officers right from the start. Their collective expertise will help us customize AERIS to your organization’s unique requirements.
3. Communicate the Vision
Clearly articulate the reasons for adopting AERIS. Highlight how real-time data exchange reduces patient delays, enhances safety, and improves overall workflows. Transparency in communication promotes collaboration and enthusiasm.
4. Comprehensive Support by HelixBeat
Helixbeat offers extensive training resources, documentation, and customer support to guide you through the process. Utilize these tools to address challenges and gain confidence in using AERIS.
5. Measure and Celebrate Success
Track key performance metrics like faster lab result processing or improved patient discharge times before and after implementation. Recognizing and celebrating achievements motivates teams and sustains progress.
Final Words
Integrating Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) with enterprise systems can change healthcare into a more efficient, patient-focused, and outcome-driven industry. By breaking down silos of fragmented data, healthcare organizations can streamline workflows, enhance operational efficiency, and deliver better care.
Solutions like AERIS play a vital role in facilitating this transformation. With real-time data sharing, advanced analytics, and secure interoperability, AERIS enables healthcare providers to bridge communication gaps, adapt to evolving needs, and reduce administrative burdens.
If you’re ready to revolutionize your healthcare systems, AERIS offers the tools and flexibility to make integration seamless and impactful. Whether you’re aiming to enhance patient outcomes, streamline operations, or align with regulatory standards, AERIS can help you achieve these goals. Contact us today to explore how AERIS can transform your healthcare ecosystem for a better tomorrow.
FAQs
1. What is EMR interoperability, and why is it important in healthcare?
EMR interoperability refers to the ability of electronic medical records systems to exchange and interpret patient information seamlessly across different healthcare platforms. By facilitating real-time access to critical patient data, healthcare providers can improve efficiency and accuracy.
2. What are the main challenges of isolated EMR systems in healthcare?
Fragmented data, communication gaps, and operational inefficiencies are common challenges in isolated EMR systems. These issues result in delayed care, repeated tests, and increased administrative burdens.
3. How does integrating EMRs with enterprise systems benefit patients?
Integration benefits patients by facilitating faster diagnoses, tailored treatment plans, and streamlined care. For example, access to a patient’s complete medical history in emergencies empowers healthcare providers to make accurate, life-saving decisions.
4. How does EMR integration improve operational efficiency in healthcare?
EMR integration simplifies workflows by automating repetitive tasks like insurance verification, appointment scheduling, patient record updates, etc. Therefore, it reduces paperwork, minimizes manual errors, and frees up healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care.
5. What role does patient engagement play in healthcare system integration?
When patients can access their medical records, track their health data, and schedule appointments easily, they feel more involved in their care. This empowerment leads to better compliance with treatment plans and improved health outcomes.
6. What are the best practices for successfully integrating EMRs with enterprise systems?
Best practices include:
- Conducting a thorough needs assessment to identify key challenges.
- Selecting a provider that adheres to healthcare interoperability standards like HL7 and FHIR.
- Implementing the integration in phases to reduce disruptions.
Engaging stakeholders and seeking regular feedback also leads to smoother adoption.
7. How does integration help healthcare organizations meet regulatory compliance?
Integrated systems enhance compliance by using secure data-sharing protocols, such as encryption and role-based access controls. They streamline adherence to regulations like HIPAA, thus keeping patient data secure while simplifying reporting and audits.
8. What technological features are essential for seamless EMR integration?
Key features include:
- Real-time data exchange.
- Compatibility with diverse protocols (e.g., HTTP, FHIR).
- Modular flexibility to integrate new systems and devices.
- Advanced analytics, automation, and strong security measures are also critical for smooth and efficient integration.
9. What is AERIS, and how does it support healthcare integration?
AERIS is a robust solution designed for seamless data sharing across healthcare systems. It enhances healthcare interoperability with features like real-time updates, standardized data formats, and AI-driven analytics. In addition, its modular design enables healthcare providers to scale and adapt as their needs evolve.